What Is The Most Important Organelle In An Animal Cell
Animate being CELL BIOLOGY
Cells are the structural and functional unit of all living organisms. Some organisms, such as bacteria, are unicellular , consisting of a single cell. Other organisms, such as humans, are multicellular , or have many cells�an estimated 100,000,000,000,000 cells! Each cell tin can take in nutrients, catechumen these nutrients into energy, comport out specialized functions, and reproduce as necessary. Even more amazing is that each cell stores its own set of instructions for carrying out each of these activities.
Cell Organization
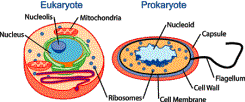
It is important to know what organism the cell comes from. There are 2 general categories of cells: prokaryotes and eukaryotes . Prokaryotes are capable of inhabiting almost every place on the earth, from the deep body of water, to the edges of hot springs, to merely nearly every surface of our bodies. Prokaryotes also lack any of the intracellular organelles and structures that are characteristic of eukaryotic cells. Most of the functions of organelles, such as mitochondria and the Golgi apparatus, are taken over past the prokaryotic plasma membrane. Eukaryotes are well-nigh x times the size of a prokaryote and can be every bit much every bit 1000 times greater in volume. The major and extremely significant difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bounded compartments in which specific metabolic activities accept place, and have modest specialized structures called organelles that are dedicated to performing certain specific functions. Most important amid these is the presence of a nucleus , a membrane-delineated compartment that houses the eukaryotic prison cell�southward Deoxyribonucleic acid.
Cell Structures: The Basics
The Plasma Membrane�A Cell's Protective Coat
The outer lining of a eukaryotic cell is called the plasma membrane . This membrane serves to divide and protect a jail cell from its surrounding environs and is fabricated mostly from a double layer of proteins and lipids, fat-like molecules. Embedded within this membrane are a diverseness of other molecules that act every bit channels and pumps, moving different molecules into and out of the cell. A course of plasma membrane is also constitute in prokaryotes, but in this organism it is unremarkably referred to as the cell membrane .
The Cytoskeleton�A Cell'due south Scaffold
The cytoskeleton is an of import, circuitous, and dynamic jail cell component. It acts to organize and maintain the cell'south shape; anchors organelles in place; helps during endocytosis (the uptake of external materials by a cell); and moves parts of the cell in processes of growth and motility. At that place are a neat number of proteins associated with the cytoskeleton, each controlling a cell�s structure by directing, bundling, and adjustment filaments.
The Cytoplasm�A Jail cell'south Inner Infinite
Inside the cell in that location is a large fluid-filled space called the cytoplasm , sometimes called the cytosol . In prokaryotes, this space is relatively free of compartments. In eukaryotes, the cytosol is the "soup" inside which all of the jail cell'southward organelles reside. It is also the home of the cytoskeleton. The cytosol contains dissolved nutrients, helps pause downwards waste products, and moves material around the cell. The nucleus often flows with the cytoplasm changing its shape as it moves. The cytoplasm also contains many salts and is an excellent conductor of electricity, creating the perfect environment for the mechanics of the cell. The function of the cytoplasm, and the organelles which reside in it, are disquisitional for a cell's survival.
Genetic Textile
Two unlike kinds of genetic material be: deoxyribonucleic acrid (DNA) and ribonucleic acrid (RNA). Nearly organisms are made of Deoxyribonucleic acid, just a few viruses have RNA as their genetic material. The biological information contained in an organism is encoded in its DNA or RNA sequence.
Prokaryotic genetic cloth is organized in a elementary circular structure that rests in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic genetic cloth is more than complex and is in units called genes . The nuclear genome is divided into 24 DNA molecules, each contained in a different chromosome .
Organelles
The human being body contains many unlike organs, such as the eye, lung, and kidney, with each organ performing a unlike function. Cells also accept a set of "little organs", called organelles , which are adapted and/or specialized for carrying out one or more vital functions. Organelles are found only in eukaryotes and are always surrounded by a protective membrane. It is of import to know some basic facts virtually the post-obit organelles.
The Nucleus�A Cell's Eye
The nucleus is the most conspicuous organelle found in a eukaryotic jail cell. It houses the prison cell's chromosomes and is the place where almost all Dna replication and RNA synthesis occurs. The nucleus is spheroid in shape and separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear envelope . The nuclear envelope isolates and protects a jail cell'due south DNA from various molecules that could accidentally damage its construction or interfere with its processing.
The Ribosome�The Protein Production Machine
Ribosomes are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The ribosome is a big complex composed of many molecules, including RNA and proteins, and is responsible for processing the genetic instructions carried by mRNA. Protein synthesis is extremely important to all cells, and therefore a big number of ribosomes�sometimes hundreds or even thousands�can be plant throughout a cell.
Ribosomes float freely in the cytoplasm or sometimes bind to another organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum.
Mitochondria--The Ability Generator
Mitochondria are cocky-replicating organelles that occur in various numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria contain their own genome that is separate and distinct from the nuclear genome of a cell. Mitochondria have two functionally distinct membrane systems separated by a space: the outer membrane, which surrounds the whole organelle; and the inner membrane, which is thrown into folds or shelves that project in. These inwards folds are chosen cristae . The number and shape of cristae in mitochondria differ depending on the tissue and organism in which they are establish, and serve to increase the surface surface area of the membrane. Mitochondria play a critical role in generating energy in the eukaryotic jail cell, and this process involves a number of complex pathways. They are the powerhouses of the prison cell.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum and the Golgi Apparatus�Macromolecule Managers
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the send network for molecules targeted for certain modifications and specific destinations, as compared to molecules that will bladder freely in the cytoplasm. The ER has two forms: the rough ER and the smooth ER . The rough ER is labeled as such because it has ribosomes adhering to its outer surface, whereas the smooth ER does not. The shine ER serves as the recipient for those proteins synthesized in the rough ER. Proteins to exist exported are passed to the Golgi appliance , sometimes called a Golgi trunk or Golgi complex , for further processing, packaging, and ship to a variety of other cellular locations.
Lysosomes and Peroxisomes�The Cellular Digestive System
Lysosomes and peroxisomes are often referred to as the garbage disposal system of a cell. Both organelles are somewhat spherical, spring by a single membrane, and rich in digestive enzymes , naturally occurring proteins that speed up biochemical processes. For example, lysosomes can contain more than three dozen enzymes for degrading proteins, nucleic acids, and certain sugars called polysaccharides. Here nosotros can see the importance behind compartmentalization of the eukaryotic cell. The cell could not business firm such destructive enzymes if they were not contained in a membrane-bound system.

Animal Cell
 |
Note: The creature eukaryotic cell concept map is based upon this article, and these two are meant either to be given out as homework or to be done in class equally a team do to fill in the concept map blanks. I think it is best utilized as a normal homework assignment to clarify in the students� minds exactly how the parts of the cell are connected.
Source: https://www.bu.edu/gk12/nishant/cellbioarticle.htm
Posted by: beckfign1986.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Most Important Organelle In An Animal Cell"
Post a Comment